Understanding Electrical Substations
April 23, 2024
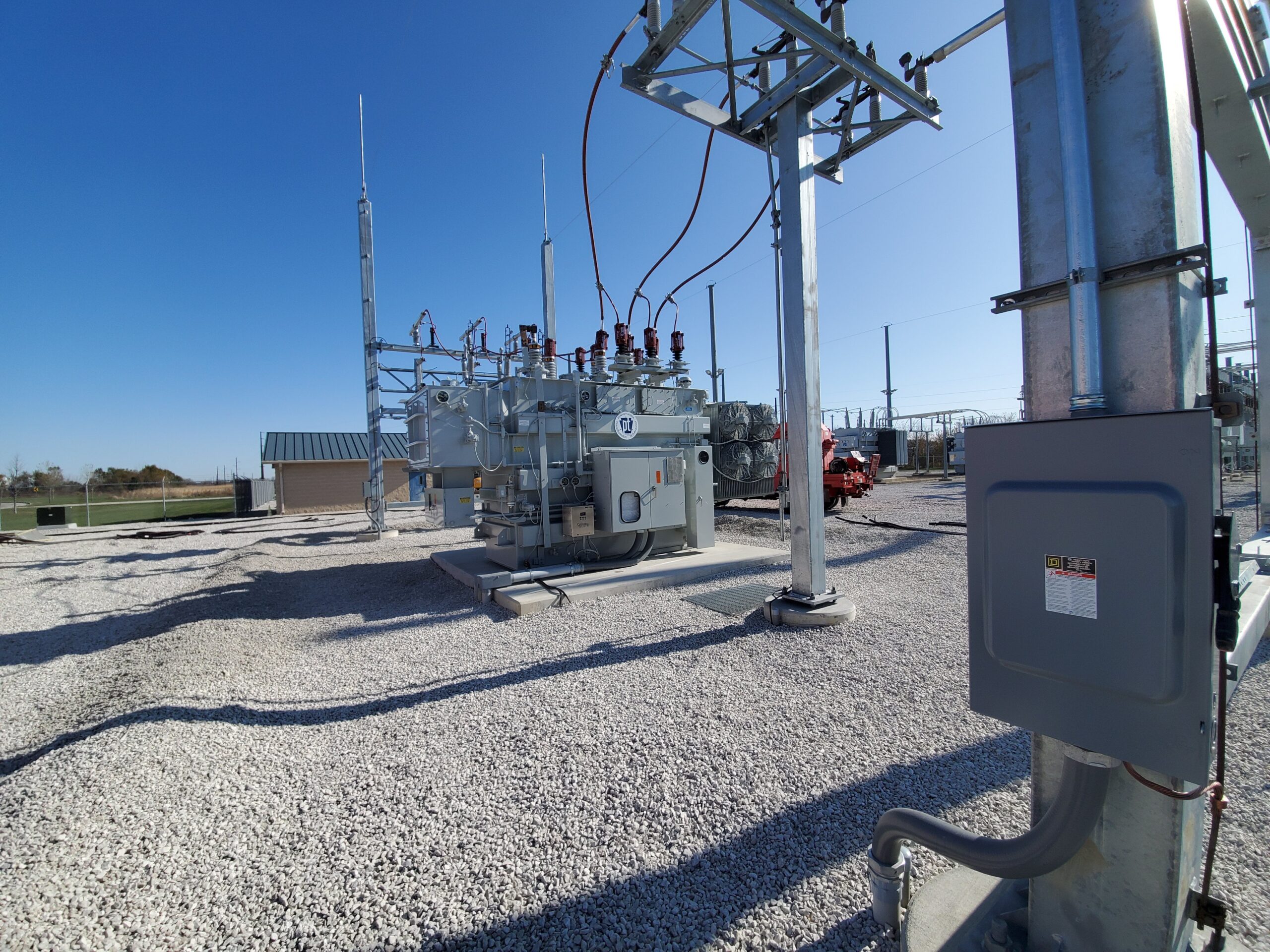

Electrical substations play a critical role in ensuring efficient and reliable power distribution. These facilities act as pivotal points within electrical networks, facilitating the transmission, distribution, and management of electrical energy.
This guide explores the purpose of substations and their importance to help you understand critical role in electrical systems, especially in industrial settings.
What is a substation?
A substation is a key component of an electrical network that facilitates the transformation of voltage levels, switching of electrical circuits, and distribution of power from transmission systems to end-users.
Substations ensure the safe and efficient transmission of electricity across different voltage levels, making it compatible with various industrial machinery and equipment. Essentially, substations play a key role in adapting and delivering electrical power effectively within an infrastructure.
What is the difference between a substation and a power station?
The difference between a substation and a power station lies in their primary functions within the electrical grid:
Power Station:
- A power station, also known as a generating station or power plant, is where electricity is generated from various energy sources such as coal, natural gas, nuclear fuel, hydroelectric dams, wind turbines, or solar panels.
- The main function of a power station is to convert mechanical or chemical energy into electrical energy through generators. This electricity is then transmitted over high-voltage transmission lines to substations.
- Power stations are typically located away from urban areas and are large-scale facilities designed specifically for electricity generation.
Substation:
- A substation is a part of the electrical grid that acts as an intermediary between the power station (or transmission system) and the end-users (homes, businesses, industries).
- The primary function of a substation is to transform voltage levels, switch electrical circuits, and distribute electrical power to different regions at suitable voltage levels for consumption.
- Substations receive high-voltage electricity from power stations or transmission lines and reduce the voltage to safer and usable levels for local distribution.
Substations also play a crucial role in maintaining grid stability, managing power flow, and ensuring electrical safety and reliability.
Substation Types & Design
There are different designs and types of substations that are tailored to meet the specific needs of electrical power systems, ensuring reliable and efficient transmission, distribution, and control of electricity across various voltage levels and operational scenarios within the grid.
Here’s an overview of common substation types and design considerations:
Transmission Substations:
Transmission substations are critical in the high-voltage transmission network, where electricity is received from power plants or other transmission substations at high voltages and then transmitted over long distances to distribution substations or large industrial consumers.
Transmission substations typically include transformers, circuit breakers, and other equipment to manage voltage levels and ensure efficient transmission.
Types of transmission substations include:
- Step-Up Substations: Step-up substations are located near power plants. They increase the voltage of electricity generated by generators, making it suitable for long-distance transmission over high-voltage lines. These substations use large transformers for voltage stepping.
- Step-Down Substations: Step-down substations are closer to end-users. They receive electricity at high voltages from transmission lines and lower the voltage to safer levels for distribution to homes, businesses, and industries. Step-down substations use transformers to reduce the voltage.
Distribution Substations:
Distribution substations serve as intermediaries between transmission systems and distribution networks. They receive electricity from higher-voltage transmission lines and further step down the voltage to levels appropriate for local distribution.
Collector Substations:
Collector substations are used in renewable energy systems such as wind farms or solar power plants. They collect electricity generated by multiple turbines or panels and step up the voltage for transmission to the main grid via transmission lines.
Substation Design Considerations:
- Layout and Arrangement: Substation layout is designed to optimize space utilization and ensure efficient flow of electrical components. Components such as transformers, circuit breakers and control systems are strategically arranged based on functional requirements and safety considerations. Circuit breakers play a crucial role in substation design by interrupting faulty currents and isolating sections of the electric power system during abnormal conditions.
- Voltage Levels: Substations are designed to handle specific voltage levels based on the requirements of the electrical network. Transformers are used to step-up or step-down voltages as needed for transmission and distribution.
- Safety and Security: Substation design incorporates safety measures such as fencing, grounding systems, and protective enclosures to prevent unauthorized access and ensure personnel safety.
- Reliability and Redundancy: Redundant components and backup systems are integrated into substation designs to minimize downtime and ensure continuous operation of critical infrastructure.
- Environmental Considerations: Substations are designed to comply with environmental regulations and minimize impact on surrounding ecosystems. Measures such as noise reduction, landscaping, and eco-friendly construction materials are implemented where applicable.
- Automation and Control Systems: Modern substations utilize automation and remote-control systems for efficient operation and monitoring. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems allow for centralized control and real-time monitoring of substations remotely.
Electrical substation operators need access to advanced designs and tools that assist in generating and maintaining electricity grids. This capability enables them to effectively manage, monitor, and control electricity.
Our Quad Plus team are experienced with specialist knowledge to help design, install and maintain your electrical substation infrastructure and power systems. Get in touch to talk to us about your substation design and automation needs.